Autotrophic Nutrition In India
Autotrophic Nutrition in India: Understanding the Essential Role of Self-Nourishing Organisms
Autotrophic nutrition is a fundamental biological process where organisms produce their own food using inorganic substances. This mode of nutrition is crucial for sustaining life on Earth, including the ecosystems found across India. From the lush forests to agricultural fields, autotrophic organisms play a vital role in the environment. This article explores the concept of autotrophic nutrition, its significance in India, and its impact on various ecosystems and agriculture.
Introduction to Autotrophic Nutrition
1. What is Autotrophic Nutrition?
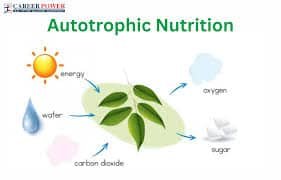
Autotrophic nutrition is the process by which organisms create their own food from simple inorganic substances. These organisms, known as autotrophs, utilize light energy (photoautotrophs) or chemical energy (chemoautotrophs) to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds.
2. Types of Autotrophic Nutrition
- Photoautotrophs: These organisms, such as plants and algae, use sunlight for photosynthesis to produce their own food.
- Chemoautotrophs: These organisms, including certain bacteria, obtain energy from chemical reactions to synthesize organic compounds.
Autotrophic Nutrition in Indian Ecosystems
1. Role in Indian Forests
In India’s diverse forests, autotrophic plants and algae are foundational to the ecosystem. Forests like the Western Ghats and the Sundarbans rely on these organisms for oxygen production and as a primary food source for herbivores.
2. Importance in Aquatic Systems
Indian rivers, lakes, and coastal waters host various autotrophic organisms, including phytoplankton and seaweeds. These organisms form the base of aquatic food chains and contribute to the oxygenation of water bodies.
Agricultural Significance
1. Photosynthesis in Indian Agriculture
In Indian agriculture, photosynthetic plants are essential for crop production. Major crops such as rice, wheat, and pulses depend on the process of photosynthesis to grow and produce food.
2. Enhancing Agricultural Practices
Understanding autotrophic nutrition helps in improving agricultural practices. Techniques such as crop rotation and the use of green manures can enhance soil health and support the productivity of autotrophic plants.
Impact on Indian Biodiversity
1. Supporting Wildlife
Autotrophic organisms are crucial in supporting India’s rich biodiversity. Herbivores, which are vital for the survival of carnivores, depend on these organisms for food. The health of ecosystems, including national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, is closely linked to the health of autotrophic species.
2. Conservation Efforts
Efforts to conserve forests, wetlands, and other natural habitats are essential for maintaining the balance of autotrophic organisms. Protecting these ecosystems ensures the continued availability of resources and supports biodiversity.
Educational and Research Perspectives
1. Research in Indian Institutions
Indian universities and research institutions are actively studying autotrophic nutrition to advance agricultural practices and understand ecological dynamics. Research in plant biology, marine biology, and environmental science often focuses on the roles of autotrophs in various ecosystems.
2. Educational Initiatives
Educational programs and outreach activities aim to raise awareness about the importance of autotrophic nutrition. Schools and colleges incorporate lessons on photosynthesis and plant biology to educate students about these essential processes.
Challenges and Future Directions
1. Environmental Changes
Climate change, deforestation, and pollution pose significant challenges to autotrophic organisms. Changes in temperature and carbon dioxide levels can impact photosynthesis rates and the health of ecosystems.
2. Sustainable Practices
Adopting sustainable agricultural and conservation practices is crucial for supporting autotrophic organisms. Initiatives such as afforestation, sustainable farming, and pollution control help mitigate adverse effects and promote ecological balance.
Conclusion
Autotrophic nutrition is a cornerstone of life on Earth, playing a vital role in sustaining ecosystems and supporting biodiversity. In India, autotrophic organisms are integral to both natural habitats and agricultural systems. By understanding and supporting these processes, we contribute to the health of our environment and the sustainability of our agricultural practices. Efforts to research, conserve, and educate about autotrophic nutrition will continue to be essential in maintaining the delicate balance of India’s diverse ecosystems.



